|
Introduction Advantages Networking Goals Networking Criteria Applications Common Terminology Used In Internet Network Topologies Types of Network LOCAL AREA NETWORK LAN Transmission Methods LAN Topologies LAN Devices Networking Basics OSI REFERENCE MODEL |
Some of most common topologies in use today include:
Bus:- Each node is daisy-chained (connected one right after
the other) along the same backbone, similar to Christmas Lights. Information sent
from a node travels along the backbone until it reaches its destination node.
Each end of a bus network must be terminated with a
resistor to keep the signal that is sent by a node across the network
from bouncing back when it reaches the end of the cable.
Ring:- Like a bus network, rings have the nodes daisy-
chained. The difference is that the end of the network comes back around to the
first node, creating a complete circuit. In a ring network, each node takes a
turn sending and receiving information through the use of a token. The token,
along with any data, is sent from the first node to the second node, which
extracts the data addressed to it and adds any data it wishes to send.
Then the second node passes the token and data
to the third node, and so on until it comes back around to the first node
again. Only the node with the token is allowed to send data. All other nodes
must wait for the token to come to them.
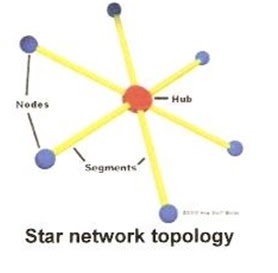
Star:- In a star network, each node is connected to central
devices called a Hub. The hub takes a single that cones from any node and
passes it along it along to all the other nodes in the network. A hub does not
perform any type of filtering or routing of the data. It is simply a junction
that joins all the different nodes together.
Star
Bus:-Probably the most common network
topology in use today, star bus ombines elements of the star and bus topologies
to create a versatile network environment. Nodes in particular areas are
connected to hubs (creating stars), and the hubs are connected together along
the network backbone (like a bus network). Quite often, stars are nested within
stars, as seen in the example below:
|
|---|
Network Topologies
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)



No comments:
Post a Comment