|
Introduction Advantages Networking Goals Networking Criteria Applications Common Terminology Used In Internet Network Topologies Types of Network LOCAL AREA NETWORK LAN Transmission Methods LAN Topologies LAN Devices Networking Basics OSI REFERENCE MODEL |
Here are some of the fundamental parts of a network:
Network: A network is a group of computers connected together
in a way that allows information to be exchanged between the computers.
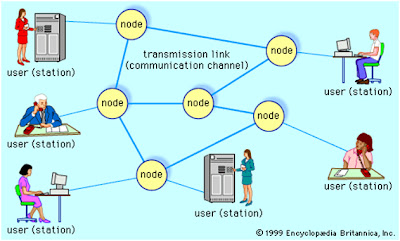
Node: A node is anything that is connected to the network.
While a node is typically a computer, it can also be something like a printer
or CD-ROM tower.
Segment: A segment is any portion of a network that is
separated, by a switch, bridge or router, from other parts of the network.
Backbone: The backbone is the main cabling of a network that
all of the segments connect to. Typically, the backbone is capable of carrying
more information than the individual segments. For example, each segment may
have a transfer rate of 10 Mbps (megabits per second), while the backbone may
operate at 100 Mbps.
Topology: Topology is the way that each node is physically
connected to the network (more on this in the next section).
Local
Area Network (LAN): A LAN is a
network of computers that are in the same general physical location, usually
within a building or a campus. If the computers are far apart (such as across
town or in different cities), than a Wide Area Network (WAN) is typically used.
Network
Interface Card (NIC): Every computer
(and most other devices) is connected to a network through an NIC. In most
desktop computers, this is an Ethernet card (normally 10 or 100 Mbps) that is
plugged into a slot on the computer’s motherboard.
Media
Access Control (MAC) Address: This is
the physical address of any device such as the NIC in a computer on the
network. The MAC address, which is made up of two equal parts, is 6 bytes long.
The first 3 bytes identify the company that made the NIC. The second 3 bytes
are the serial number of the NIC itself.
|
|---|
NETWORKING BASICS
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment